Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes, it significantly impacts patients’ lives and those of their loved ones. This article provides a detailed exploration of Alzheimer’s disease, including its causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment approaches.
1. What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of dementia cases. It is a progressive condition that slowly destroys memory and cognitive skills, ultimately interfering with the ability to perform simple tasks. The disease is named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer, who first described it in 1906 after noticing changes in the brain tissue of a woman who had died of an unusual mental illness.
2. Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some key risk factors include:
-
Age: The risk increases significantly after the age of 65.
-
Genetics: Family history and certain genes like APOE-e4 are linked to the disease.
-
Health Conditions: Cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity may increase risk.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, sedentary behavior, and poor diet can contribute.
-
Head Injuries: Traumatic brain injuries have been associated with higher risk.
Researchers are also investigating the role of beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which accumulate in the brain and disrupt normal cell function.
3. Early Symptoms and Warning Signs
Recognizing Alzheimer’s early can help in managing the disease more effectively. Common early symptoms include:
-
Memory loss that disrupts daily life, especially forgetting recently learned information.
-
Difficulty planning or solving problems.
-
Challenges in completing familiar tasks at home or work.
-
Confusion with time or place.
-
Trouble understanding visual images and spatial relationships.
-
New problems with words in speaking or writing.
-
Misplacing things and losing the ability to retrace steps.
-
Decreased or poor judgment.
-
Withdrawal from work or social activities.
-
Changes in mood and personality.
These symptoms may progress gradually and vary from person to person.
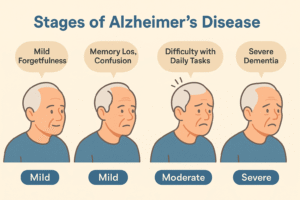
4. Progression and Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s typically progresses through several stages:
-
Preclinical Alzheimer’s: Changes in the brain occur without noticeable symptoms.
-
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): Mild but measurable memory problems appear.
-
Mild Dementia: Greater memory loss and confusion, personality changes, and difficulties with everyday tasks begin.
-
Moderate Dementia: Significant memory loss, inability to perform routine tasks without assistance, and behavioral changes.
-
Severe Dementia: Loss of ability to communicate, recognize loved ones, and perform basic activities like eating or walking.
Understanding the stages can help families plan care and treatment accordingly.

5. Diagnostic Methods
There is no single test to diagnose Alzheimer’s. Doctors use a combination of methods to determine if a patient has the disease:
-
Medical History: Gathering information about mental and physical health, medication use, and family history.
-
Neurological Exams: Testing reflexes, coordination, and balance.
-
Mental Status Tests: Assessing memory, problem-solving skills, and language abilities.
-
Brain Imaging: MRI and CT scans can identify brain atrophy, while PET scans can detect beta-amyloid plaques.
-
Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to rule out other causes of dementia-like symptoms.
Early and accurate diagnosis allows for better planning and care.
6. Treatment Options and Management
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but treatments can temporarily slow the progression of symptoms and improve quality of life. Key treatment approaches include:
-
Medications:
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors (like donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine) boost levels of neurotransmitters involved in memory and judgment.
-
Memantine regulates glutamate activity to help cognitive function.
-
-
Lifestyle Changes:
-
Regular physical exercise
-
Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids
-
Cognitive stimulation and mental exercises
-
-
Therapies:
-
Occupational therapy to adapt living spaces and routines
-
Psychological therapies to manage depression or anxiety
-
-
New Developments:
-
Monoclonal antibodies targeting beta-amyloid plaques are under study and show promise in slowing disease progression.
-
Supportive care and creating a safe environment are also crucial for patient well-being.
7. Living with Alzheimer’s: Support and Coping Strategies
Living with Alzheimer’s presents challenges, but support and planning can make a significant difference:
-
For Patients:
-
Staying socially active
-
Engaging in meaningful activities
-
Following routines to maintain independence as long as possible
-
-
For Caregivers:
-
Seeking support groups
-
Respite care to avoid burnout
-
Learning about the disease to better understand behavioral changes
-
-
Community and Resources:
-
Alzheimer’s associations offer educational programs, hotlines, and counseling.
-
Legal and financial planning is essential early in the diagnosis.
-
With the right support systems, individuals with Alzheimer’s and their families can navigate the journey with greater resilience and hope.
Please don’t forget to check our page for similar diseases and treatments.